Aluminum casting is a plastic manufacturing process with broad applications which result in the production of parts that are light but strong. Aluminum casting finds applications in multiple industries including automotive, aerospace, construction and electronic, and as such has become an integral part of modern manufacturing. This article examines the aluminum casting process, its different techniques, benefits, as well as various industries which obtain aluminum castings and their application.
To know more about Aluminum Casting- https://www.indianmetal.solutions/
What is Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting is a controlled manufacturing process whereby liquids of aluminum alloys are poured with the aid of gravity into a mold whose dimensions and shapes have already been determined. It is a productive manufacturing process that is characterized by precision tolerances, excellent surface finishes and is capable of producing a variety of intricate shapes. Aluminum has characteristics including, lightweight, corrosion-resistant, as well as a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it very fit for casting especially for bear stress where low weight and high durability are of priority in industries.
The Aluminum Casting Process
The basic aluminum casting process encompasses a number of steps which are as follows:
1. Design Steps of the Mold: The casting process commences from designing the mold itself which determines the shape of the aluminum part to be produced. The design process encompasses the type of material, which include steel, sand or ceramic from which the mold is made depending on the casting technique employed.
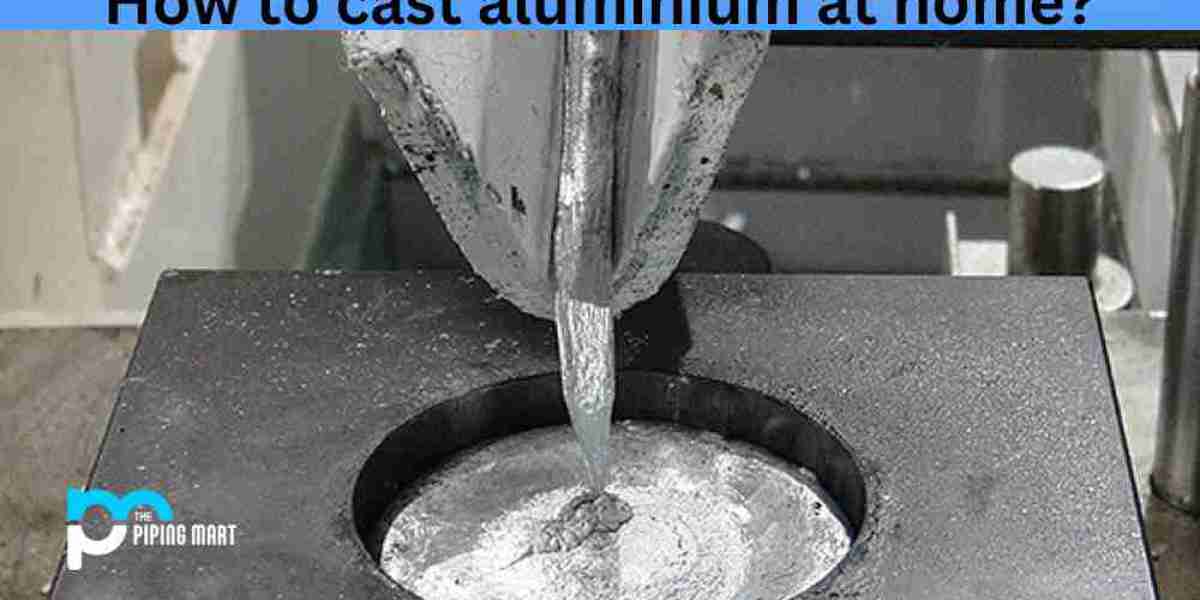
2. Getting the Aluminum to Melt: Applying heat in a furnace will melt aluminum since its melting point is approximately 660 °C (or 1220 °F). After that, it is in liquid form and is poured or injected into the already shaped mold.
3. Pouring or Injecting the Aluminum: Aluminum in melted form is poured into the proper pouring cavity or high-pressure brings it close to the cavity depending on the method used. The molten material fills each and every cavity in a liquid form and when it cools and solidifies, it retains the shape formed by the cavities.
4. Cooling and Solidifying: The solidifying molten aluminum comes in touch with the inside surface of the mold which results in the cast component attaining its final shape. Each part is harder and has been cooled at a different rate depending on the casting material and the methods where one was used in making the molds.
5. Taking Out and Finishing the Cast: Once shot blasting is done successfully, the cast aluminum part is carefully taken out of the mold. The leftover unnecessary materials are cut off, and other finishing processes like machining and polishing are done to some parts to ensure that they comply to quality requirements.
Aluminum Casting Methods
Casting aluminum can be done with a particular method depending on the final results intended. Some of the most common methods include the following:
1. Sand Casting
Sand casting includes the mixing of the aluminum product with a sand and a binding agent in a mold that can be knocked off when the aluminum has cooled. It is one of the most versatile and cheapest terrains which can be used to create large or intricate shapes. Sand casting allows for the mass production of engine blocks, parts for aerospace and components of industrial machines.
2. Die Casting
In die casting, aluminum is over injected into a steel die under pressure. This method is very productive and yields high-quality parts with ideal surface and dimensional characteristics. Die casting is useful in mass production and is thus adaptable to preparing parts such as engine housing, enclosures for electronics and automotive parts.
3. Permanent Mold Casting
Permanent mold casting makes use of metal molds which are reused, the molds are mainly in steel or iron. The process requires the use of gravity whenever molten aluminum is poured into the mold or an under low pressure process. Parts created via this method exhibit a fine grain structure and greater mechanical properties, such as those used for automotive wheels, engine pistons and cylinder heads.
4. Investment Casting (Lost Wax Casting)
This process involves the use of a wax model of the part, covering the wax model with a ceramic material, known as investment casting or lost wax casting. This ceramic shell, once solidified, has the wax melted, creating a cavity for the aluminum. This technique allows the fabrication of molds for small, intricate or gentle parts like the aerospace and medical instruments with extreme accuracy.
5. Centrifugal Casting
This method involves the introduction of a rotating mold to which molten aluminum is poured. The molten metal is pushed against the walls of the mold by centrifugal force allowing high-strength, hollow parts to be formed. This method is highly suitable for the manufacture of pipes, tubes, and other cylindrical parts with high strength and durability.
Advantages of Aluminum Casting
Aluminum casting is relatively popular in the industries for its many advantages as seen below:
1. Strong and Lightweight: Due to its high strength to weight ratio, aluminum is most suitable for components since they need not compromise on durability and weight across automotive and aerospace applications.
2. Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms an oxide layer that is protective, thus preventing corrosion from occurring. This quality makes aluminum useful in the manufacture of components that are used in outdoor or marine applications where conditions can be harsh.
3. High Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has a really good thermal conductivity which makes it a good candidate for components like heat sinks in electronics or engine parts in the automotive industries which require efficient thermal management.
4. Excellent Malleability and Machinability: Aluminium is also easy to machine and work on hence it can take on a variety of designs and patterns.
5. Economical in Nature if Produced in Large Quantities: Bello specifically mentions the economical nature of aluminum die casting, as there is a low cost with large quantities due to mold reuse and it being an efficient process.