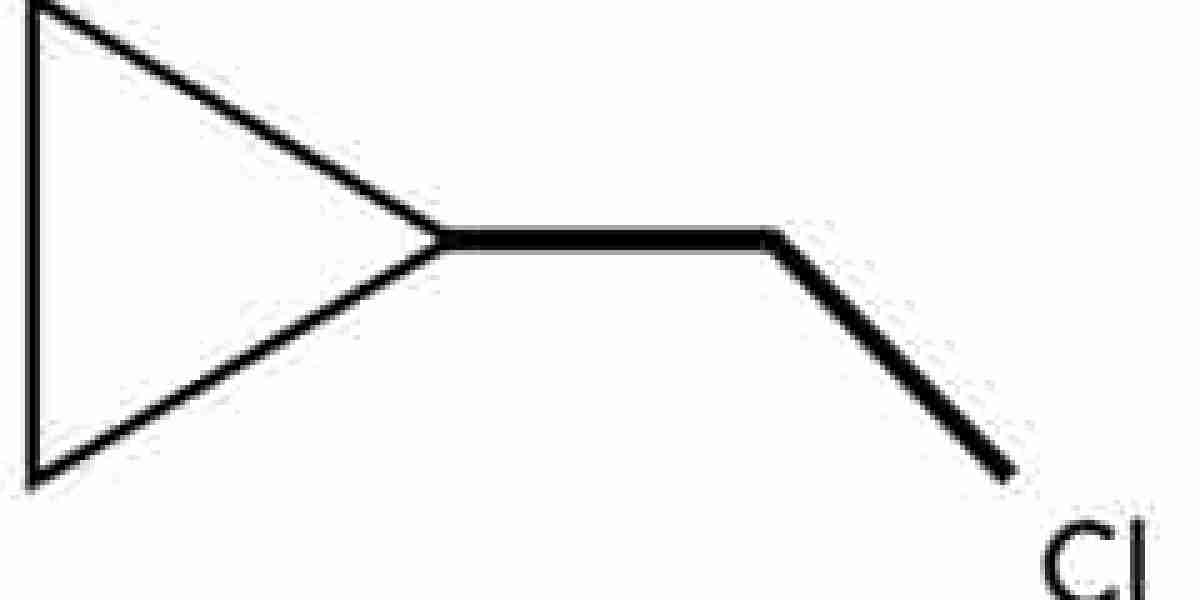
In the ever-fascinating world of organic chemistry, there exists a compound that packs a punch – both in terms of its unique structure and its versatile applications. Cyclobutyl methyl bromide, with its chemical formula C5H9Br, is a halogenated alkyl compound that has captured the attention of chemists worldwide. Let's delve into the intriguing aspects of this strained yet remarkable molecule.
The Structural Peculiarity
Cyclobutyl methyl bromide's structure is a fascinating interplay of strain and reactivity. At its core lies a cyclobutyl ring, a four-membered saturated cyclic hydrocarbon ring that defies the conventional norms of ring geometry. Unlike its larger cycloalkane counterparts, the cyclobutyl ring is strained, with ring angles of approximately 88-90 degrees, deviating significantly from the ideal tetrahedral angle of 109.5 degrees.
This ring strain is the driving force behind the unique reactivity of cyclobutyl methyl bromide and its derivatives. The strained nature of the cyclobutyl ring makes it more reactive than its unstrained counterparts, opening up a plethora of synthetic possibilities.
Cyclobutyl Methyl Bromide Structure:-
CH3
|
CH2 - C - CH2
|
CH2
|
Br
The Reactive Duo: Cyclobutyl and Bromine
In addition to the strained cyclobutyl ring, cyclobutyl methyl bromide also features a reactive bromine atom attached to one of the ring carbons. The carbon-bromine bond is relatively weak and polar, making it susceptible to cleavage under certain conditions. This reactive duo – the strained cyclobutyl ring and the bromine atom – sets the stage for a wide array of organic transformations.
Synthetic Versatility and Applications
Cyclobutyl methyl bromide's unique structural features make it a valuable intermediate in organic synthesis. It can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions, where the bromine atom is replaced by various nucleophiles, resulting in a diverse array of cyclobutane derivatives. Additionally, it can participate in elimination reactions, leading to the formation of cyclobutene compounds.
One of the key applications of cyclobutyl methyl bromide is in the preparation of cyclobutane derivatives and small-ring compounds. These compounds find applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and material science. Furthermore, cyclobutyl methyl bromide can be employed as an alkylating agent, introducing the cyclobutyl moiety into various molecules, expanding the scope of potential applications.
Safety and Handling Considerations
Despite its synthetic allure, cyclobutyl methyl bromide is a halogenated organic compound and should be handled with caution. It is an irritant to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system, and can cause burns or irritation upon exposure. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and a fume hood, is essential when working with this compound.
Storage is also a crucial aspect, as cyclobutyl methyl bromide should be kept in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from sources of ignition and incompatible materials.
Conclusion
Cyclobutyl methyl bromide is a true gem in the realm of organic chemistry, showcasing the intricate interplay between structure and reactivity. Its strained cyclobutyl ring and reactive bromine atom make it a versatile reagent in various organic transformations, opening doors to the synthesis of diverse compounds. As research continues to unravel the secrets of this remarkable molecule, its applications in fields like pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and material science hold immense potential. With proper safety measures and skilled handling, cyclobutyl methyl bromide will undoubtedly continue to captivate and inspire chemists around the globe.